BizMobile Go! Key Features
2. Support a variety of devices and thier usage
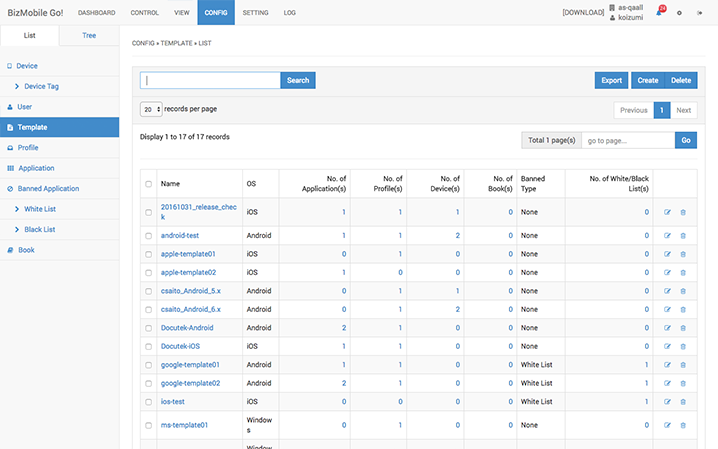
 Multiple OS and devices
Multiple OS and devices
BizMobile Go! is an MDM service that supports iOS, Android, and Windows. Even in a mixture of these OSs, you can manage them easily with a single platform. BizMobile Go! is designed in such a way that different OSs can be managed on the same interface in the same manner.
Currently, business mobile devices mainly run Apple’s iOS, which is considered to be secure and convenient. However, 2015 marked the start of a new era of choices for OSs and devices, with Google strengthening business-related functionalities with Android 5, and Microsoft releasing Windows 10.
In the iOS environment, there are shops, warehouses, and factories that use the iPod touch, but iOS generally does not have device-dependent problems due to the limited number of types of devices. However, this is different for Android and Windows OS. There are even devices that do not support MDM functions. Initially, Android for Work only ran on only Google’s Nexus devices. It is only recently that wider range of Android for Work devices were released. As Samsung Galaxy devices run on a customized OS, there is a need for special care. Android or Windows increases device dependencies, it requires compatibility verification in advance.
Google Nexus devices are constantly upgraded in a similar manner than iOS devices. Even though Google Nexus devices is priced about the same as iOS devices, they have less experience in actual enterprise usage. iOS is considered to be more secure with its extensive track record and comprehensive pool of knowledge in its operation. However, enterprises choose to use Android or Windows for different reasons. They are looking for devices to be developed with fewer capabilities and with lower pricing. In shops, warehouses and factories, they only require a limited set of functions. There are strong needs for lower priced devices dedicated for specific usage. With a prior interoperability testing to deal with device-dependent issues, enterprise IT can use Android or Windows devices with fewer hurdles.
Enterprises require multiple OS and device support when choosing MDM. Not only business devices, but devices for education also requires lower pricing. Therefore, MDM services are selected based on the support for latest device models and OS versions.
Comply with all OS standards
Support newest device models
Comply with OS version updates
 Multiple usage models
Multiple usage models
Difference between usage of smartphones and tablets and that of traditional PCs is getting clearer. We can classify mobile device usage models into the following.
COPE(Corporate-Owned, Personal-Enabled)Corporate devices with some personal usage
COCM(Corporate-Owned, Corporate-Managed)Corporate devices with restricted personal usage
COSU(Corporate-Owned, Single-Use)A company device dedicated for a specific task
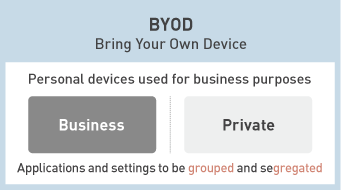
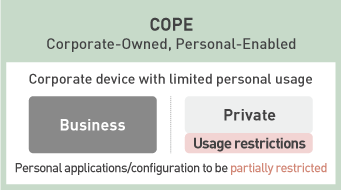
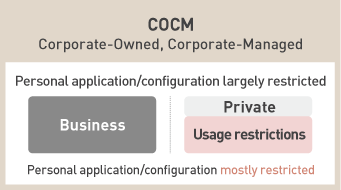
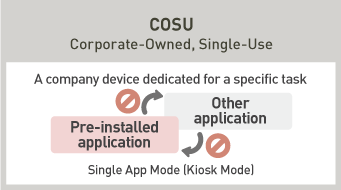
While it is possible to partially restrict personal configuration and applications, it is impossible to completely ban personal usage. However, by the segregation of enterprise data and private data, as well as appropriate restrictions on features that can be used for personal purposes, even BYOD usage model can ensure security and can be prevented from information leaks. As devices are offered by enterprises in COPE usage model, it is more common to further restrict their functions. COCM usage models greatly restrict personal usage. On top of that, COSU models allows multiple workers to use the same device, where the devices are set to “Single App Mode (Kiosk Mode)”
※To find out more about how each OS segregates corporate and personal usage, please click here.
BizMobile Go! allows you to easily specify which functions you wish to restrict for each OS, and allows you to securely protect corporate data.
| OS type | COPE (Some personal usage allowed) | COCM (Personal usage largely restricted) |
| iOS 9 | Functions that can be restricted: 47 | Functions that can be restricted: 30 (factory reset required) |
| Android 5.1 | Functions that can be restricted: 32 | Functions that can be restricted: 37 (factory reset required) |
| Windows 10 | Functions that can be restricted: 107 (partially supported and planned to be enhanced) | |
 Version updates
Version updates
iOS guarantees that the device can be used for 3 generations (i.e.3 years). Normally, changes in the API of MDM services are notified well in advance so as in the OS version updates. MDM API specifications are released just before or a little after OS release. Though BizMobile has to run testing after each API specification release, in the past 5 years, the fatal bugs that we have discovered and reported to Apple were only 3 cases. Having less bugs as compared to other OSs is one of the advantages of using iOS.
However, applications are different. Applications are immediately affected after changes to OS specifications. Generally, specifications for a new OS will be announced 3 months before its release, and a beta version will be provided for testing. This is why popular applications on the App Store are able to adapt quickly when a new OS is released. In-house MDM applications may become unusable if support for a new OS is not achieved within this period. Major updates will put a huge burden on the MDM vendor. In addition, on-premise MDM services may face larger trouble as services are customized for each individual customer, as bug fixing, response to flaws, and addition of new functionalities need to be taken care for each customer. We have seen cases where MDM providers had to request not to update OSs until modifications to the application were completed. In-house MDM service makes company IT administrators nervous whenever an OS version update occurs.
Currently, the biggest problem lies in applications that are developed in-house (also known as in-house enterprise applications by Apple). However, most of the problems are coming from issues in the companies who are developing the in-house applications and in the companies who order these applications. Most business application vendors have experience in Windows and Linux systems, but not in iOS and Android applications. They may not know that there are large OS version updates every year, and that applications must be modified to be compatible with new OS versions. Those update information are provided through events like WWDC and through developer websites, that are only available in English. Many developers are also not well-versed in English environment, so there are times when support cannot be achieved in the 3-month grace period as well. In fact, there are some cases that enterprises cannot prepare the right budget, or even worse, cannot estimate how long and how much it costs to update. Therefore, some enterprises consider to cease OS version updates. This could be possible for devices in Supervised Mode, but is not recommended from the security perspective.
MDM APIs that met OS standards before Android 5 were fewer and had limited functionality, as compared to iOS. Hence, there were no device dependent issues for MDM services providing only the basic functions (like BizMobile Go!). However, many MDM services have developed in-house applications to expand security functionality of devices. Such applications may depend highly on the device models and OS versions, and were compatible with a limited number of devices with limited functionality had a detailed list of bugs. Therefore, large enterprise have decided not to use Android devices for their employees.
Google made large changes in the OS in Android 5. Due to these changes, even domestic carriers selling Android 5 devices initially did not support Android for Work functions. This caused Google Nexus devices to be the only devices where Android for Work functions were guaranteed. In 2016, some devices sold by NTT DoCoMo and KDDI support Android for Work and Device Owner Mode.
Domestic Android devices have been able to provide update support only for approx. 2 generations. This is because domestic device manufacturers and mobile operators have made their own modifications to the OS. This is a considerably fatal flaw for business devices because they cannot update OSs to solve bugs and to avoid vulnerabilities. The problem lies in the fact that huge OS changes have continued to be made throughout the 2 generations of Android 5 and 6, thus impacting application vendors and MDM vendors. The scale of changes is such that an MDM service that worked with Android 5 will not be able to work normally on Android 6.
Microsoft is also challenging mobile OS as well. It aims to make a comeback with Windows 10 and quickly catch up to iOS and Android 5. Windows 10 has finally attained the same sandbox structure as that of iOS and Android. With strict specifications that manufacturers must fulfill, and device manufacturers making no modifications to the OS, Windows 10 keeps device dependencies to a minimum, though not as low as iOS. Compared to Windows 10, Android is open-source, so mobile carriers and device manufacturers are free to modify the OS, thus ironically creating devices for which version updates are hard to implement. Windows 10 works in a very different way from Windows 8.1, so when a device registered on an MDM service is upgraded to Windows 10, MDM services for Windows 8.1 become unable to function and the device must be registered on the MDM service once again.
BizMobile Go! has a policy of using standard OS functions, so it is one of the few MDM services that are largely unaffected by OS version updates. The system is designed to minimize usage of customized MDM application that offers proprietary functions. But when OS changes are substantial, such as migrating from Android 5 to Android 6 or migrating from Windows 8.1 to Windows 10, it is affected to some extent. And there appear to be many devices that are unable to support the new functions of Windows 10, much like how few devices supported Android for Work previously. It seems like we have to wait a while more for devices that are equipped with functions that rely on hardware instead.
Summary of BizMobile Go! specifications
| Service | Functionality provided | Functions | Usage purposes | iOS 9 |
And-roid 6 |
Win 10 Desktop |
|||
| Monitoring | Anti-theft, anti-loss measures | Prevention of unauthorized access | Automatic kitting | ||||||
| Standard | User management | Organization/group management functions | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Device management | Usage status dashboard | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| Log management | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||
| Alarm notifications | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||
| Device restrictions | Make passcode policy compulsory (for local lock & wipe) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| Remote lock | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | - | ||||
| Remote wipe | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| Remove passcode | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | - | ||||
| Selective wipe (wipe only business-related data) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| Access control (allow display and operation based on restrictions) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| Lock device to prevent usage (administrator lock) | ○ | ○ | *1 | ◎ | *1 | ||||
| Settings management | Batch distribution (settings) | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | ||||
| Batch distribution (certificates authenticated with password) | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | |||||
| Batch distribution (individual device configuration) (Note: Use of CSV) | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | |||||
| Setting restrictions | Separation of enterprise and private data, blocking of data transfer | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | |||
| Encryption of enterprise data | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | |||||
| Compulsory encrypted backup | ○ | ○ | - | - | |||||
| Remove enterprise data from list of backup items | ○ | ○ | - | - | |||||
| Restrict personal usage partially | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | |||||
| Restrict personal usage greatly | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | *1 | |||||
| Web filtering (whitelists, blacklists, plugins) | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | *1 | |||||
| Global proxy (specific communication channels) | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | - | |||||
| Always-on VPN connection | ○ | ◎ | *1 | *1 | |||||
| Block factory reset | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | *1 | ||||
| Use of DEP (Device Enrollment Program) | ○ | ◎ | - | - | |||||
| Block deletion and bypassing of MDM (Note: Only when DEP is used) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ○ | |||
| Application management | Batch purchase (Store application licenses) | ○ | ○ | *1 | *1 | ||||
| Batch distribution (in-house applications, App Store applications) (Note: By user) | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | |||||
| Batch distribution (in-house applications, App Store applications) (Note: By device) | ○ | ○ | - | - | |||||
| Batch distribution (individual application configuration) (Note: Application is required to be compatible with this feture) | ○ | ○ | - | - | |||||
| Detection of blocked applications (whitelists, blacklists) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | ||||
| Application restrictions | Per-App VPN (force VPN connection only for specific applications) | ○ | ○ | *1 | *1 | ||||
| Authorize installation of App Store applications | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ○ | *1 | |||
| Block automatic downloads of App Store applications | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ○ | *1 | |||
| Silent installation/deletion of applications (App Store applications) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | *1 | *1 | |||
| Block deletion of applications | ○ | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | *1 | |||
| Dedicated device modes (Single App Mode, Kiosk Mode) | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | *1 | |||||
| Content management | Batch distribution of files to iBook (enterprise data, e-books) | ○ | ○ | - | - | ||||
| Deletion of files in iBook (enterprise data, e-books) | ○ | ○ | ○ | - | - | ||||
| Options | Messages | Collect/display location information | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | |
| Simultaneous message notification (read status can be monitored) | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | |||||
| Jailbreak notification (for jailbreaking, rooting) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | - | ||||
| Personal | Personal UI (for Self Service) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| Personal IVR (for service over telephones) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||
| Support for special cases | Device exchange | Device exchange service (automatic transfer of configuration to new device and subsequent reset of the old device) | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | |||
| Setting restrictions | Secured camera | ○ | ○ | ◎ | *1 | *1 | |||
| Geofence (GPS, Wi-Fi, iBeacon) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | *1 | *1 | |||
| ◎ | Devices in Supervised Mode |
| − | Function not provided by OS |
| *1 | Development planned |